LIGHT
Light is a form of energy which gives us the sensation of vision.
Rectilinear propagation of light- The property of light travelling in a straight line is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Beam of light- It is the stream of light and is shown by a number of rays all of which may be parallel or diverging or converging.
Reflection of light- The process of sending back the rays of light which fall on the surface of an object.
Mirror- Any polished or shiny surface can act as a mirror.
Lateral inversion- In an image formed by a mirror, the left side of the object is seen as the right side of the image and right side of the objects is seen as the left side of the image.
Write the differences between real image and virtual image.
REAL IMAGE
➤It can be obtained on a screen.
➤It is inverted.
➤It is formed when rays of light actually meet at a point on the screen after reflection.
VIRTUAL IMAGE
➤It can't be obtained on a screen.
➤It is erect.
➤It is formed when rays of light do not meet at a point but appear to meed after reflection.
Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
➤The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect.
➤It is of the same size as the object.
➤The image is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
➤It is laterally inverted.
Spherical Mirror- A smooth and polished curved surface which reflects light. It is a part of a sphere.
Convex Mirror(draw diagram)- IF the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is curved outward, it is called a convex mirror.
Concave Mirror(draw diagram)- IF the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is curved inwards, it is called a concave mirror.
➤The nature and size of the image formed by a concave mirror depends on the distance of the object from the mirror.
➤For very distant objects, a concave mirror produces a real and inverted image, which is smaller than the object.
➤As the distance of the object is reduced gradually, by bringing it more and more towards the concave mirror the image remains real and inverted but its size is increasing. When the object is placed very close to the concave mirror, the image formed is virtual anderect and enlarge.
Uses of concave mirror➤The reflectors of torches, headlight of cars and scooters are concave in shape.
➤Dentist use concave mirrors to see enlarged image of the teeth.
➤They are used as shaving mirrors and makeup mirrors.
➤Doctors use concave mirrors for examining eyes, nose, ears and throat.
➤Concave mirrors can concentrate the suns rays at a point. So, they are used in solar power projects.
Characteristics of an image formed by a convex mirror.➤The image formed by a convex mirror is virtual, erect and diminished.
Uses of Convex mirror
➤Convex mirror is used as rear view in cars or vehicles. They give a wider field of view. As compared to that of a plane mirror. Hence the driver of the car can see a larger area behind the car when he looks into the rear view mirror in front of him. It also gives an erect image smaller than the object.
➤They are used in supermarkets parking lot etc to get a larger field of view.
"OBJECTS IN THE MIRROR ARE CLOSER THAN THEY APPEAR." Why is this warning message put on rear view mirrors of cars?
Convex mirrors give a wider field of view and also makes objects appear smaller. Since smaller appearing objects seem farther away than they actually are, a driver might make a mistake during lane change assuming that adjacent vehicle is at a safe distance behind when in fact it is quite closer.
Lenses- A piece of transparent material (glass or plastic) which has one or two spherical surfaces.
Converging and diverging lenses. (draw diagram)
A convex lens converges (bend inward) the light generally falling on it and it is called converging lens. A concave lens diverges (bends outward) the light and is called diverging lens.
CONCAVE LENS
➤A lens which is thicker at the edges and thinner in the middle.
➤When held close to the object, it forms a virtual, erect and diminished image.
➤When held away from the object it forms virtual, erect and diminished image for all positions of the object.
CONVEX LENS
➤A lens which is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges.
➤When held close to the object it forms a virtual, erect and magnified image.
➤When held away from the object it forms real and inverted image. The image may be diminished or magnified or of same size depending upon the position of the object form eh lens.
White light-Any light which is composed of 7 colours.
Dispersion of light- The splitting of white light into 7 different colours.
Spectrum- The band of 7 colours. (VIBGYOR)
Causes of Dispersion
Light of all colours travel at the same speed, but in any transparent medium like water or glass, the light of different colours travel with different speed (wavelength) Red light travels the fastest while the violet light travels the slowest. As a result red bends the least and violet the most.
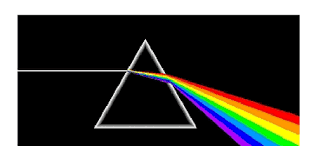
Splitting of light using prism(draw diagram)
Take a glass prism. Allow a narrow beam of sumlight through a small hole in the window of a dark room to fall on one face of the prism. Let the light coming out of the other face of the prism fall on a white sheet of paper or on a white wall. We obsever that white light splits into 7 colours. This shows that the sunlight consist of 7 colours. The sunlight is said to be white light.
Newton's disc
Take a circular cardboard disc. Divide this disc into 7 segments. Paint the seven rainbow colours on these segments. Make a small hole at the centre of the disc. Fix the disk loosely on the tip of a refill of a pen. If you rotat the disc fast enough the colours merges and appear whitish.
Uses of concave mirror➤The reflectors of torches, headlight of cars and scooters are concave in shape.
➤Dentist use concave mirrors to see enlarged image of the teeth.
➤They are used as shaving mirrors and makeup mirrors.
➤Doctors use concave mirrors for examining eyes, nose, ears and throat.
➤Concave mirrors can concentrate the suns rays at a point. So, they are used in solar power projects.
Characteristics of an image formed by a convex mirror.➤The image formed by a convex mirror is virtual, erect and diminished.
Uses of Convex mirror
➤Convex mirror is used as rear view in cars or vehicles. They give a wider field of view. As compared to that of a plane mirror. Hence the driver of the car can see a larger area behind the car when he looks into the rear view mirror in front of him. It also gives an erect image smaller than the object.
➤They are used in supermarkets parking lot etc to get a larger field of view.
"OBJECTS IN THE MIRROR ARE CLOSER THAN THEY APPEAR." Why is this warning message put on rear view mirrors of cars?
Convex mirrors give a wider field of view and also makes objects appear smaller. Since smaller appearing objects seem farther away than they actually are, a driver might make a mistake during lane change assuming that adjacent vehicle is at a safe distance behind when in fact it is quite closer.
Lenses- A piece of transparent material (glass or plastic) which has one or two spherical surfaces.
Converging and diverging lenses. (draw diagram)
A convex lens converges (bend inward) the light generally falling on it and it is called converging lens. A concave lens diverges (bends outward) the light and is called diverging lens.
CONCAVE LENS
➤A lens which is thicker at the edges and thinner in the middle.
➤When held close to the object, it forms a virtual, erect and diminished image.
➤When held away from the object it forms virtual, erect and diminished image for all positions of the object.
CONVEX LENS
➤A lens which is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges.
➤When held close to the object it forms a virtual, erect and magnified image.
➤When held away from the object it forms real and inverted image. The image may be diminished or magnified or of same size depending upon the position of the object form eh lens.
White light-Any light which is composed of 7 colours.
Dispersion of light- The splitting of white light into 7 different colours.
Spectrum- The band of 7 colours. (VIBGYOR)
Causes of Dispersion
Light of all colours travel at the same speed, but in any transparent medium like water or glass, the light of different colours travel with different speed (wavelength) Red light travels the fastest while the violet light travels the slowest. As a result red bends the least and violet the most.
Splitting of light using prism(draw diagram)
Take a glass prism. Allow a narrow beam of sumlight through a small hole in the window of a dark room to fall on one face of the prism. Let the light coming out of the other face of the prism fall on a white sheet of paper or on a white wall. We obsever that white light splits into 7 colours. This shows that the sunlight consist of 7 colours. The sunlight is said to be white light.
Newton's disc
Take a circular cardboard disc. Divide this disc into 7 segments. Paint the seven rainbow colours on these segments. Make a small hole at the centre of the disc. Fix the disk loosely on the tip of a refill of a pen. If you rotat the disc fast enough the colours merges and appear whitish.











No comments:
Post a Comment